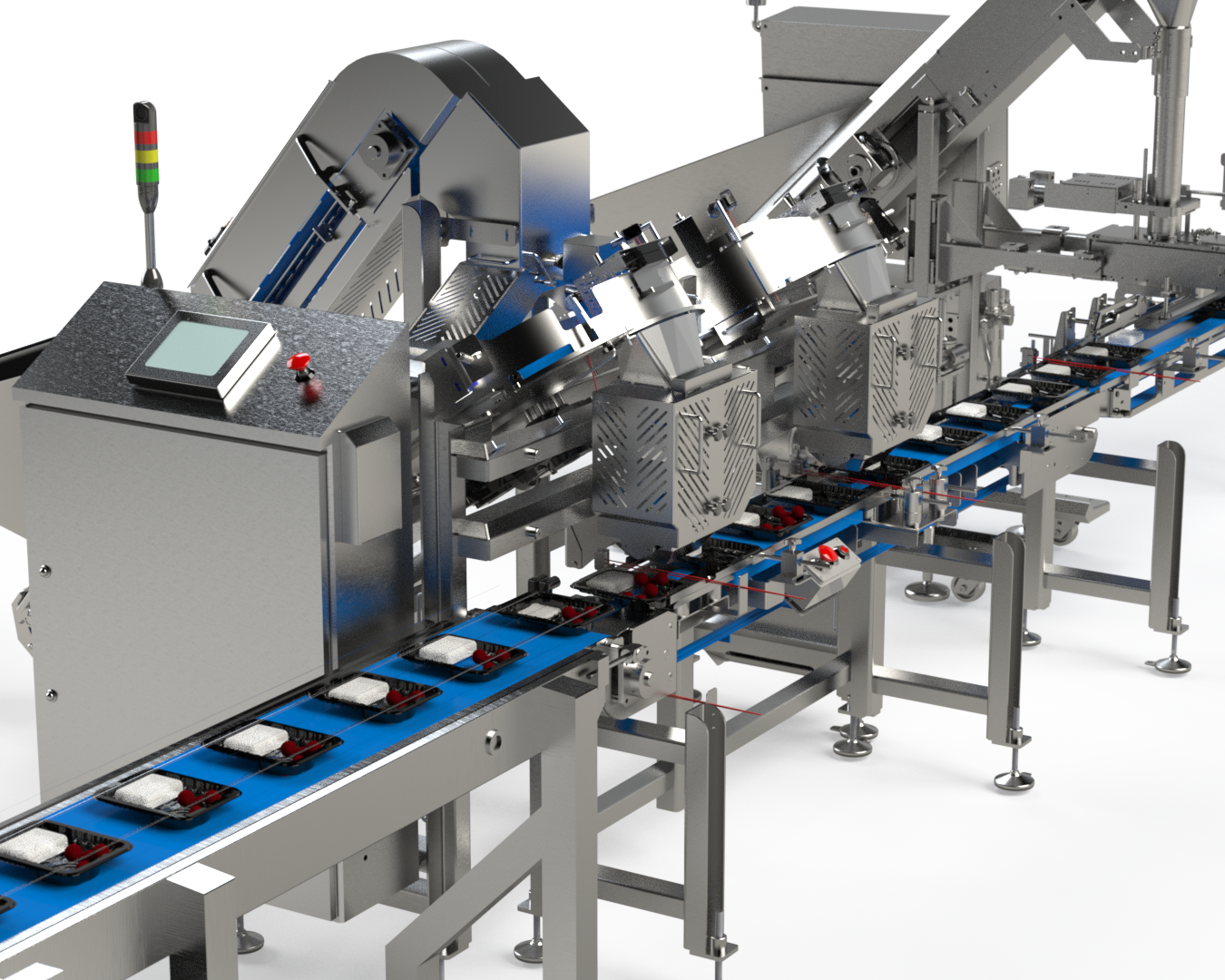
Filling Systems for Food Manufacturers

In the fast-paced world of food manufacturing, precision, efficiency, and consistency are more important than ever. As consumer demand grows for high-quality packaged products, manufacturers face increasing pressure to optimize their production lines. One critical element in meeting these demands is selecting and utilizing the right filling systems—specialized machines that ensure products are accurately portioned, packaged, and ready for market.
From sauces and soups to powders and beverages, modern filling systems cater to a vast array of food products. But with so many options available, how do you determine which system is right for your business? This guide dives into the intricacies of filling systems, exploring their types, applications, and benefits. You’ll discover how these systems enhance production efficiency, reduce waste, and maintain compliance with food safety standards.
Whether you’re an engineer designing a new production line, a technical manager seeking to improve operations, or a buyer evaluating equipment options, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Let’s unpack the world of filling systems and reveal how they can transform your food manufacturing process.
What Are Filling Systems?
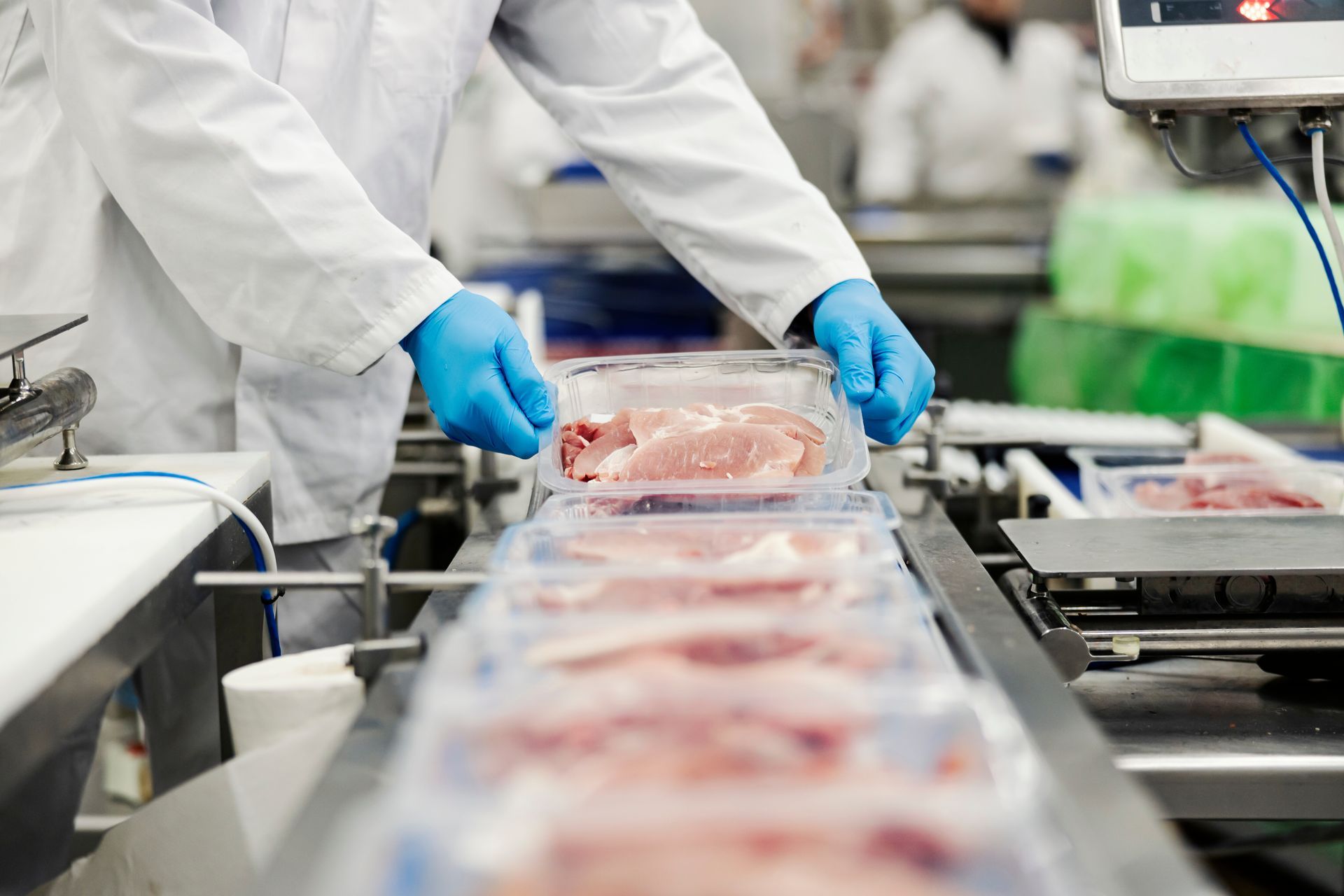
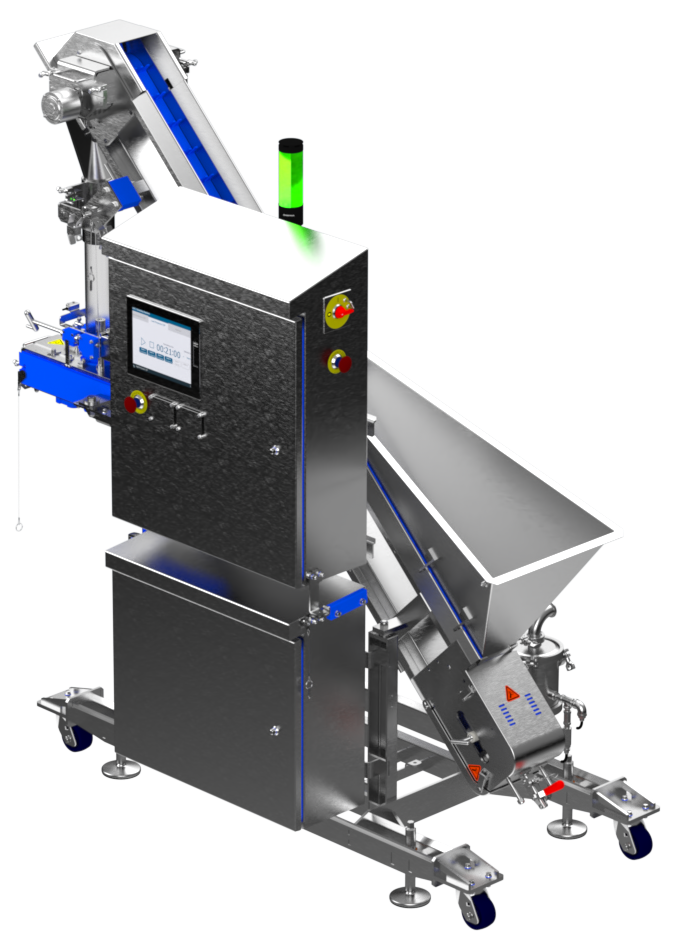
Filling systems are specialized machines used in food manufacturing to measure and dispense precise quantities of products into packaging. These systems play a crucial role in ensuring consistency, reducing waste, and maintaining product quality. Whether you’re filling a pouch of granola or a bottle of hot sauce, filling systems are designed to handle the unique properties of various products and packaging formats.
There are different types of filling systems, each tailored to specific needs. For instance, liquid filling systems are ideal for beverages and sauces, while auger fillers work best for powders like spices or protein mixes. The versatility of these systems allows food manufacturers to streamline operations and scale production without sacrificing accuracy or efficiency.
One unique aspect often overlooked is the role of food-grade materials in filling systems. Machines must meet stringent hygiene standards to prevent contamination, especially in industries like dairy or ready-to-eat meals. This means choosing equipment made from stainless steel and other non-reactive materials, which are easy to clean and sanitize.
By understanding the fundamentals of filling systems, you’ll be better equipped to identify the right technology for your production line, ensuring your processes are both efficient and compliant with industry standards.
Types of Filling Systems
Food manufacturers can choose from various filling systems based on their product type and production needs. These include volumetric, gravimetric, liquid, and auger fillers. Each system offers unique benefits tailored to specific applications.
Volumetric Filling Systems
- Dispense a precise volume of product, making them ideal for items like sauces, jams, or dressings.
- Known for speed and reliability, especially in high-throughput environments.
Gravimetric Filling Systems
- Use weight to determine the exact quantity, excelling in precision.
- Perfect for granular products like rice or nuts, where accuracy is critical to meeting consumer expectations.
Liquid Filling Systems
- Designed for products like beverages or oils.
- Common designs include:
- Overflow fillers for consistent bottle levels.
- Piston fillers for thicker liquids like syrups or purees.
Auger Fillers
- Ideal for powders and granular products.
- Ensure smooth, spill-free filling, perfect for protein powders or spices.
When selecting a system, consider not only the product’s physical properties but also your operational goals. For example, a small business might opt for a semi-automatic liquid filler to save costs, while a large-scale manufacturer might prioritize high-speed rotary systems to meet demand.
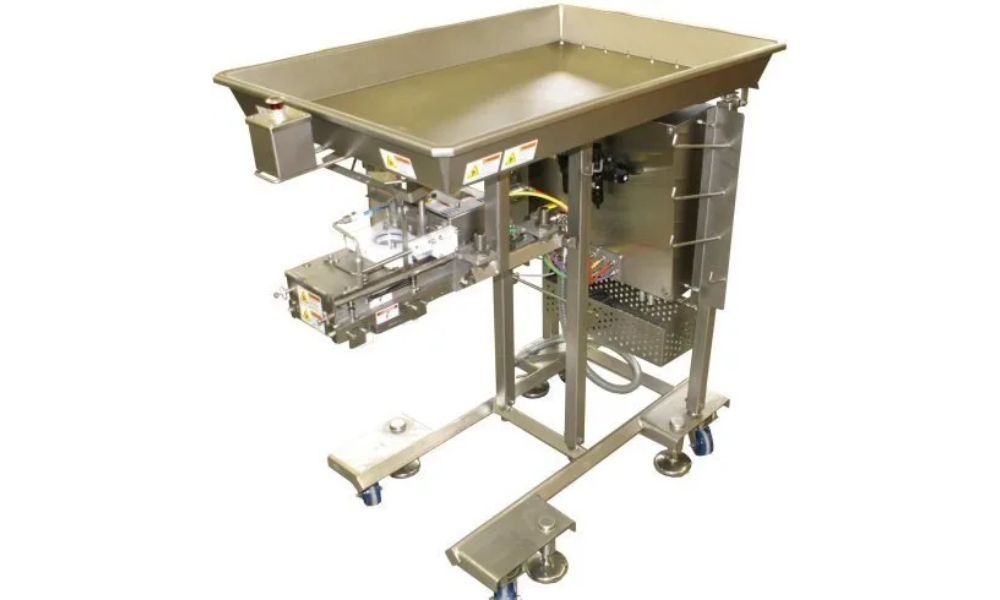
Key Components of Filling Systems
Every filling system consists of several critical components that work together to ensure smooth and accurate operation. Understanding these components can help manufacturers maintain their equipment and optimize performance.
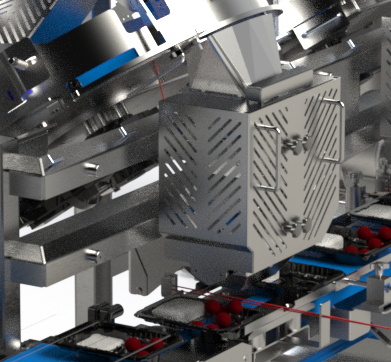
Filling Heads and Mechanisms
- The heart of the system, determining how the product is dispensed.
- Depending on the system, filling heads may use gravity, pistons, or augers to move the product into packaging.

Conveyors and Product Handling
- Ensure packaging moves efficiently through the filling process.
- Modern systems often include automated adjustments to handle different container sizes and shapes, adding flexibility.

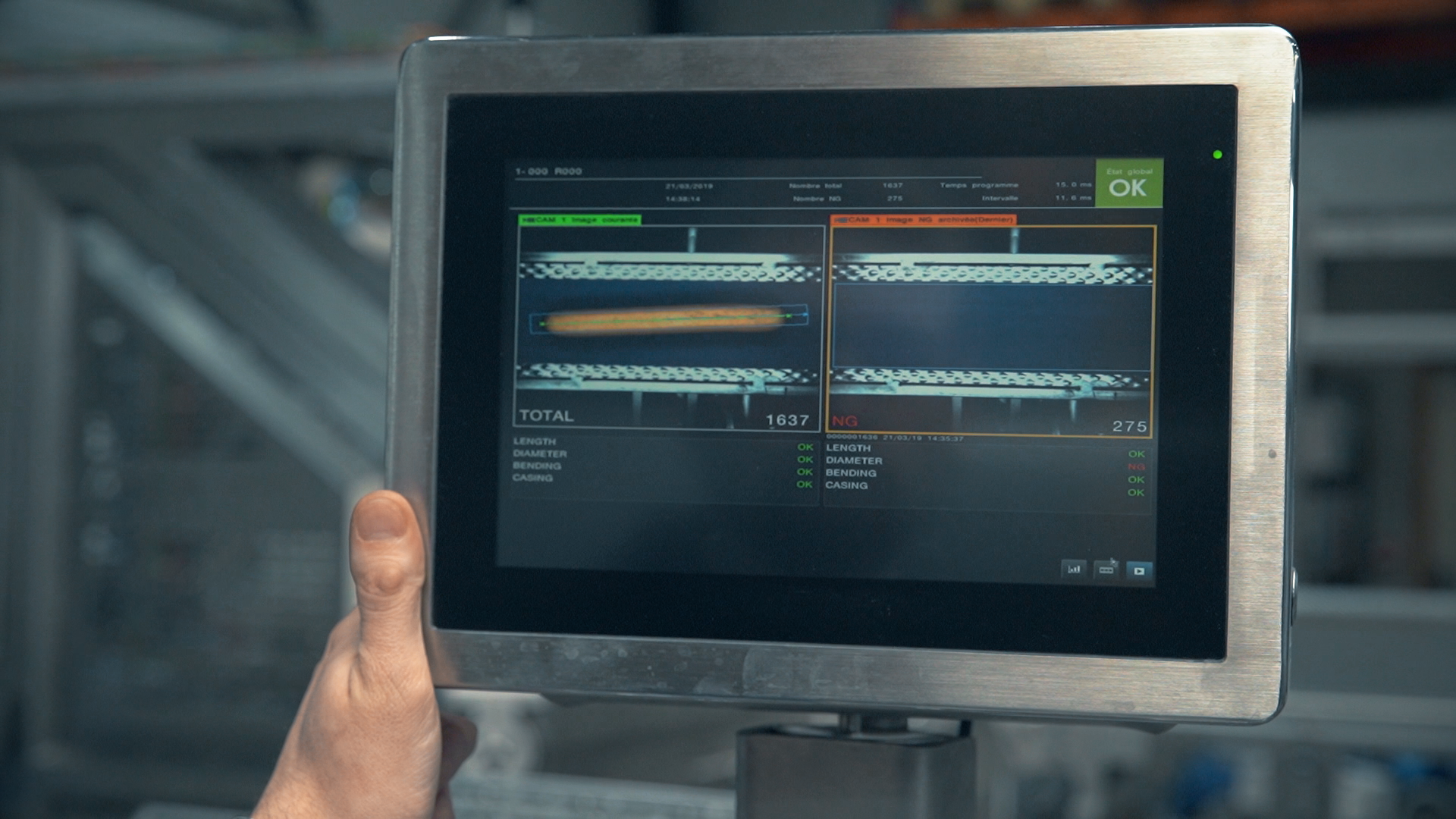
Control Systems and Automation
- Advanced filling systems include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that allow fine-tuning for speed, volume, and accuracy.
- IoT technology integration enables real-time performance monitoring, helping manufacturers detect issues before they become costly downtime.
Choosing the Right Filling System for Your Needs
Selecting the right filling system involves evaluating your unique production needs and long-term goals.
Factors to Consider
1. Product Type: Liquids, powders, or solids all have distinct requirements. For instance:
- Liquid products with varying viscosities may need piston fillers.
- Granular foods like rice might benefit from gravimetric systems.
2. Production Volume:
- High-speed rotary systems suit large-scale operations.
- Smaller businesses may prefer semi-automatic systems for cost-effectiveness.
3. Automation Level:
- Fully automated systems minimize labor costs but require a larger investment upfront.
- By weighing these factors carefully, you can align your choice with both immediate and long-term production goals.
Benefits of Modern Filling Systems
Modern filling systems offer significant advantages for food manufacturers.
- Accuracy: Ensures consistent product quantities, reducing overfilling and underfilling.
- Efficiency: Automated features handle high volumes with minimal downtime.
- Compliance: Designed with food-grade materials to meet strict hygiene standards.
- Sustainability: Minimize waste and energy usage, meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly practices.
By investing in advanced filling systems, manufacturers not only streamline operations but also position themselves for long-term growth.
FAQs About Filling Systems
1. What types of filling systems are best for liquid food products?
Liquid food products like sauces, oils, and beverages are best handled by liquid filling systems, such as overflow or piston fillers. The choice depends on the viscosity of your product and your production speed requirements.
2. How do volumetric filling systems work?
Volumetric filling systems dispense a precise volume of product using a piston or rotary pump mechanism, making them ideal for sauces or dressings.
3. What is the difference between volumetric and gravimetric filling systems?
Volumetric systems measure by volume, while gravimetric systems measure by weight. Volumetric fillers are faster; gravimetric systems are more precise.
4. How can I maintain hygiene standards with filling systems?
Choose machines with food-grade materials and automated cleaning features. Regular maintenance and compliance protocols are key.
5. Can filling systems handle multiple product types?
Yes, modern systems are versatile and can handle liquids, powders, and granules with customizable settings.
Ready to optimize your food manufacturing processes? Explore advanced filling systems tailored to your production needs and take the next step toward precision and efficiency.
References
1. Multi-Fill.
Food Filling Machines.
2. Inline Filling Systems.
Packaging Equipment Overview.
3. AMS Filling Systems.
Custom Filling Solutions.
4. Accutek Packaging.
Liquid Filling Machines.
5. VKPAK.
Filling Systems: The Ultimate Guide.
Designing a food filling line: Product is king